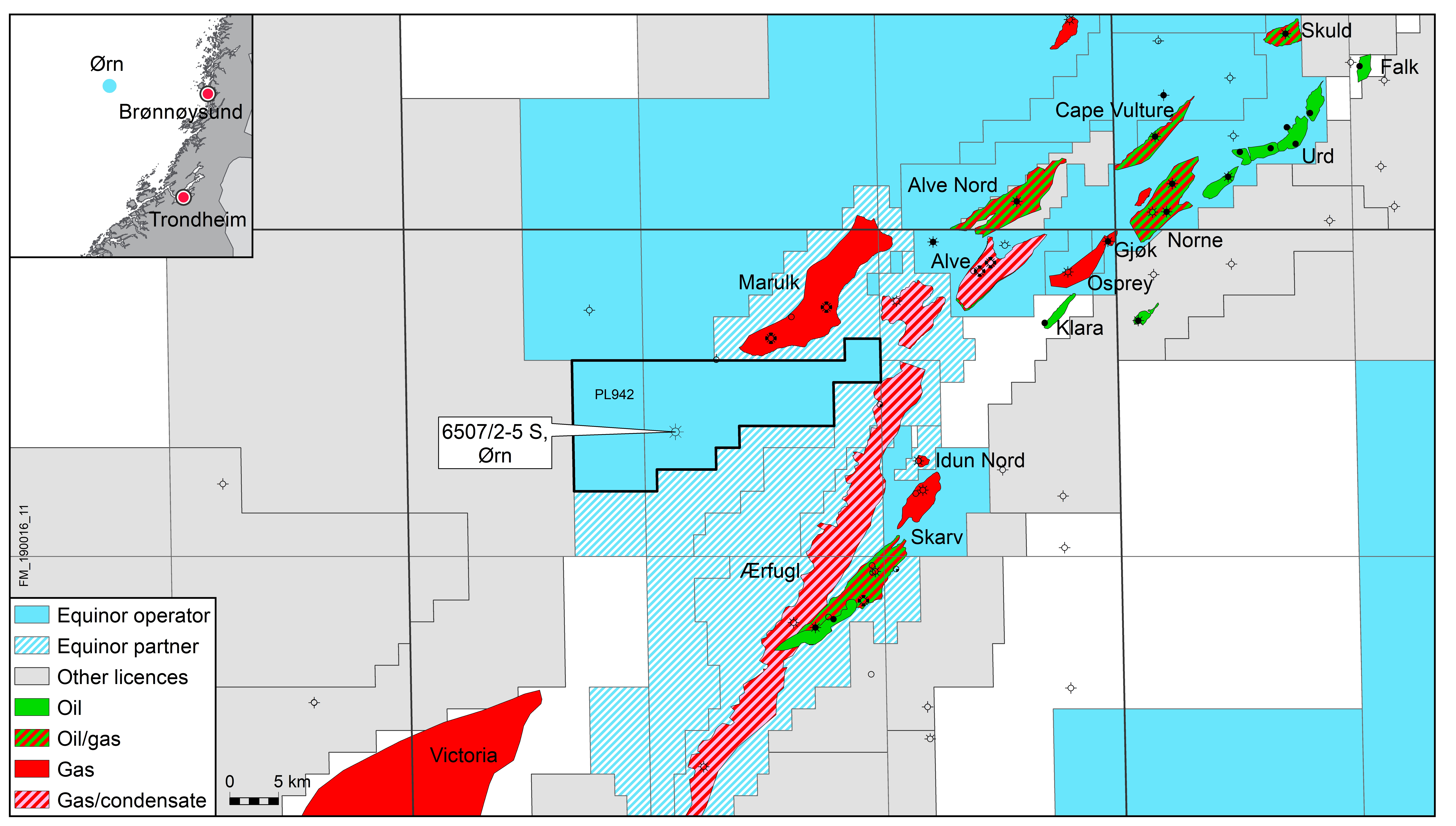
Equinor and its partners AkerBP and Wellesley Petroleum have found gas in the Ørn exploration well south-west of the Marulk field in the Norwegian Sea. Recoverable resources are estimated at 8–14 million standard cubic metres of oil equivalent, corresponding to 50–88 million barrels of oil equivalent (boe).
“This is good news. The Ørn discovery proves that there are still opportunities on the Norwegian continental shelf and reconfirms the Norwegian Sea’s importance to our domestic activity,” says Nick Ashton, Equinor’s senior vice president for exploration in Norway and the UK.
Exploration well 6507/2-5 S in production licence (PL) 942 was drilled around 12 kilometres south-west of the Marulk field, 38 kilometres south-west of the Norne field and 20 kilometres north-west of Skarv. The partnership will evaluate the discovery and clarify the need for delineation.
“The discovery follows several discoveries we have made in the same area during the past years, adding considerable volumes in an area with an already developed infrastructure. This gives us the opportunity to recover the resources profitably for both the licensees and society,” says Ashton.
In June, Equinor announced the Snadd Outer Outer/Black Vulture oil and gas discoveries south-west of the Norne field. Since 2017, Equinor has been operator of or partner in several discoveries in the Norwegian Sea totalling an estimated volume of 200-650 million boe.
6507/2-5 S is the first exploration well in PL942, which was included in the 2017 awards in predefined areas (APA). The licensees are Equinor (operator, 40%), AkerBP (30%) and Wellesley (30%).
Drilled by the West Phoenix drilling rig to a vertical depth of 4147 metres below sea level, the well was concluded in the Tilje formation in Early Jurassic rocks. Water depth in the area is 332 metres.
The well has been permanently plugged and abandoned.